Introduction
INSPIRE is the world's largest stroke perfusion imaging registry, with >8000 stroke patients with advanced imaging and clinical data from Australian, Chinese, Canadian, Japanese and Indian centres.
Aims
- Measure outcomes of advanced CT stroke imaging.
- Assess whether the implementation of quality use of advanced CT imaging improves the safe and effective delivery of reperfusion treatment.
- Develop a Quality Assurance Framework for advanced CT imaging in stroke with standardisation of the post-processing and reporting of advanced CT.
Leadership Team: INSPIRE is led by Professor Mark Parsons and Dr Longting Lin, supported by Dr Chushuang Chen as the global project manger.
Overview
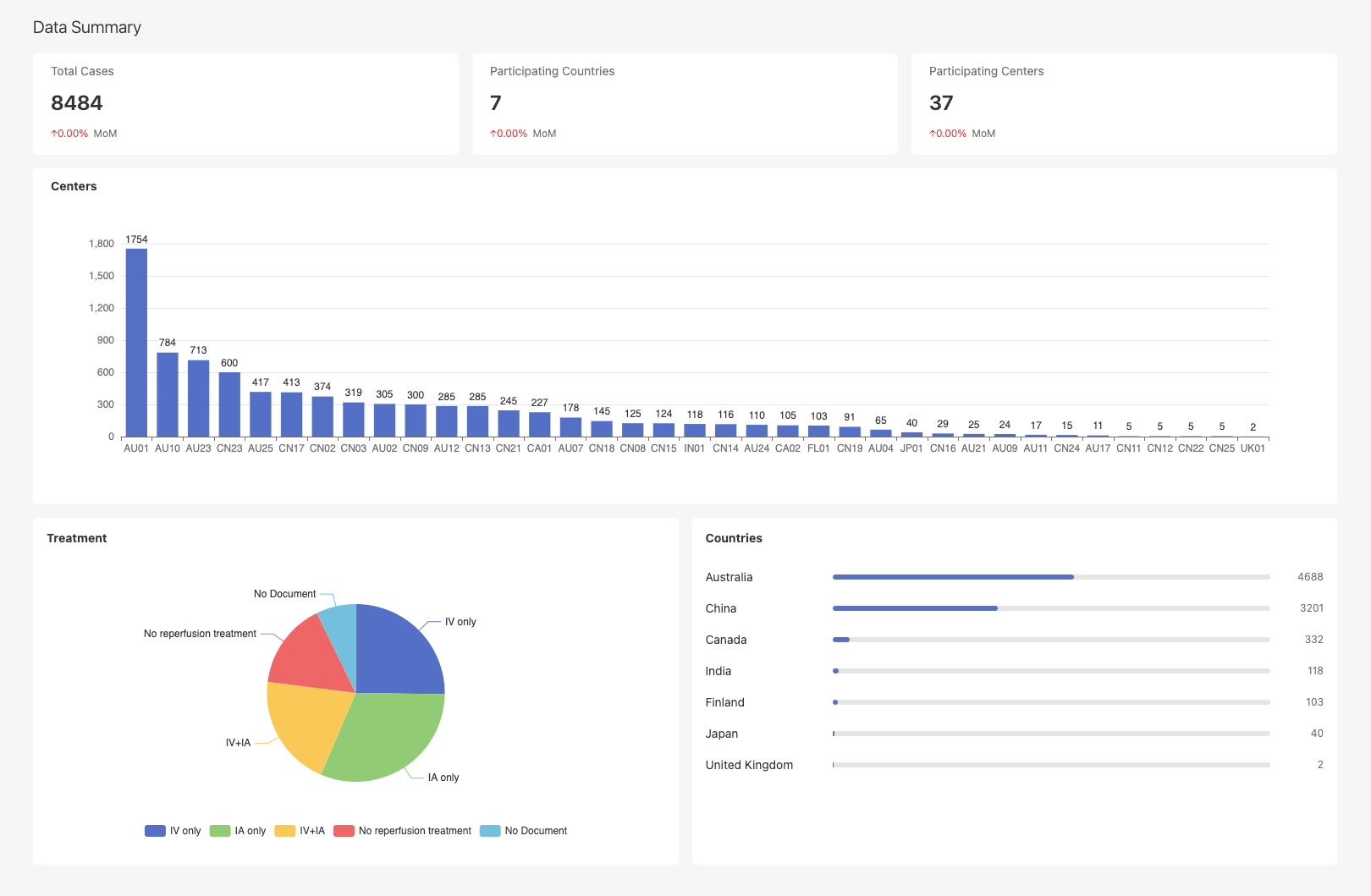
Data Summary
Publications
Sui Y, Chen W, Chen C, et al. CTP-Defined Large Core Is a Better Predictor of Poor Outcome for Endovascular Treatment Than ASPECTS-Defined Large Core. Stroke 2024; 55(5): 1227-34.
Lin L, Wang Y, Chen C, et al. Exploring ischemic core growth rate and endovascular therapy benefit in large core patients. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2024; 44(12): 1593-604.
Sun J, Werdiger F, Blair C, et al. Automatic segmentation of hemorrhagic transformation on follow-up non-contrast CT after acute ischemic stroke. Front Neuroinform 2024; 18: 1382630.
Wang P, Chen W, Chen C, et al. Association of Perfusion Lesion Variables With Functional Outcome in Patients With Mild Stroke and Large Vessel Occlusion Managed Medically. Neurology 2023; 100(6): e627-e38.
Lin L, Zhang H, Liu F, et al. Bridging Thrombolysis Before Endovascular Therapy in Stroke Patients With Faster Core Growth. Neurology 2023; 100(20): e2083-e92.
Sarraj A, Parsons M, Bivard A, et al. Endovascular Thrombectomy Versus Medical Management in Isolated M2 Occlusions: Pooled Patient-Level Analysis from the EXTEND-IA Trials, INSPIRE, and SELECT Studies. Ann Neurol 2022; 91(5): 629-39.
Garcia-Esperon C, Bivard A, Johns H, et al. Association of Endovascular Thrombectomy With Functional Outcome in Patients With Acute Stroke With a Large Ischemic Core. Neurology 2022; 99(13): e1345-e55.
Lin L, Zhang H, Chen C, et al. Stroke Patients With Faster Core Growth Have Greater Benefit From Endovascular Therapy. Stroke 2021; 52(12): 3998-4006.
Lin L, Yang J, Chen C, et al. Association of Collateral Status and Ischemic Core Growth in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology 2021; 96(2): e161-e70.
Lin L, Chen C, Tian H, et al. Perfusion Computed Tomography Accurately Quantifies Collateral Flow After Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020; 51(3): 1006-9.
Chen C, Parsons MW, Levi CR, et al. What Is the "Optimal" Target Mismatch Criteria for Acute Ischemic Stroke? Front Neurol 2020; 11: 590766.
Tian H, Parsons MW, Levi CR, et al. Influence of occlusion site and baseline ischemic core on outcome in patients with ischemic stroke. Neurology 2019; 92(23): e2626-e43.
Tian H, Chen C, Garcia-Esperon C, et al. Dynamic CT but Not Optimized Multiphase CT Angiography Accurately Identifies CT Perfusion Target Mismatch Ischemic Stroke Patients. Front Neurol 2019; 10: 1130.
Hong L, Cheng X, Lin L, et al. The blood pressure paradox in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 2019; 85(3): 331-9.
Chen C, Parsons MW, Levi CR, et al. Exploring the relationship between ischemic core volume and clinical outcomes after thrombectomy or thrombolysis. Neurology 2019; 93(3): e283-e92.
Chen C, Bivard A, Lin L, Levi CR, Spratt NJ, Parsons MW. Thresholds for infarction vary between gray matter and white matter in acute ischemic stroke: A CT perfusion study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019; 39(3): 536-46.
Lin L, Bivard A, Kleinig T, et al. Correction for Delay and Dispersion Results in More Accurate Cerebral Blood Flow Ischemic Core Measurement in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2018; 49(4): 924-30.
Lin L, Cheng X, Bivard A, Levi CR, Dong Q, Parsons MW. Quantifying reperfusion of the ischemic region on whole-brain computed tomography perfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2017; 37(6): 2125-36.
Chen C, Parsons MW, Clapham M, et al. Influence of Penumbral Reperfusion on Clinical Outcome Depends on Baseline Ischemic Core Volume. Stroke 2017; 48(10): 2739-45.
Lin L, Bivard A, Krishnamurthy V, Levi CR, Parsons MW. Whole-Brain CT Perfusion to Quantify Acute Ischemic Penumbra and Core. Radiology 2016; 279(3): 876-87.
About INSPIRE
We welcome global research centers and hospitals to join the INSPIRE project, to jointly promote stroke perfusion imaging research.